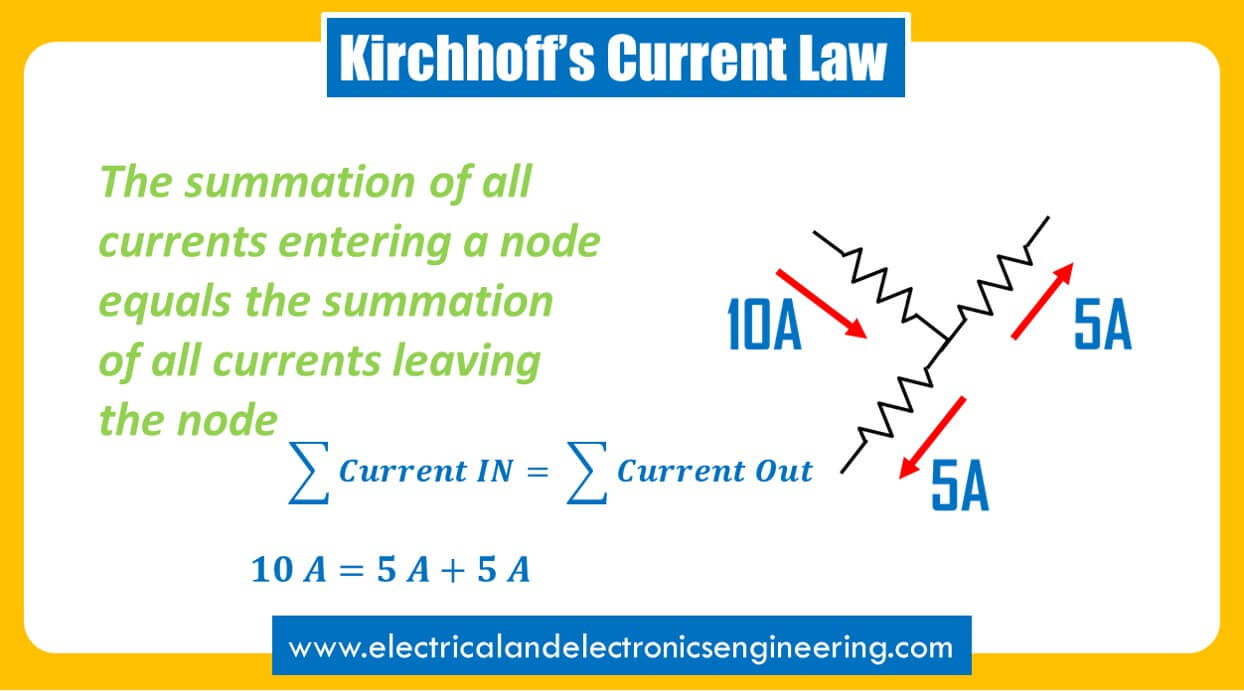
Kirchhoff’s Current Law is one of the fundamental laws in Electrical and Electronics Engineering. Also known as KCL, the law explains the behavior of current in parallel circuits.
Statement: The sum of electrical current entering a node is equal to sum of current leaving the node.
Mathematically
Σ Current In = Σ Current Out
Let’s consider a circuit having three resistors:
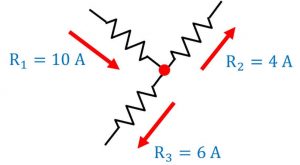
A current of 10 ampere enters the node (red dote), while a current of 6 A, and 4 A leaves the node.
Now
Σ Current In = Σ Current Out
10 A = 6 A + 4 A
10 A = 10 A
Kirchhoff’s Current Law Solved Example
Question: Find all the unknown currents in the circuit given below.
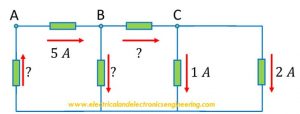
Solution: First off let’s label all the currents:
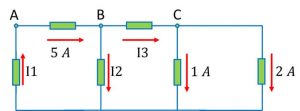
Application of KCL at node C yeilds
I3 = 1 A + 2 A
I3 = 3 A
Now application of KCL at node B yeilds
5 A = I2 + I3
5 A = I2 + 3A
I2 = 5 A – 3 A = 2 A
So I2 = 2A
Application of KCL at node A yields
I1 = 5A