Electricity is one of major necessities of our life. Our mobile phones, electronics appliances, cooling/heating systems rely on electricity.
Did you ever wondered How and where this electricity is generated or how it travels towards our homes?
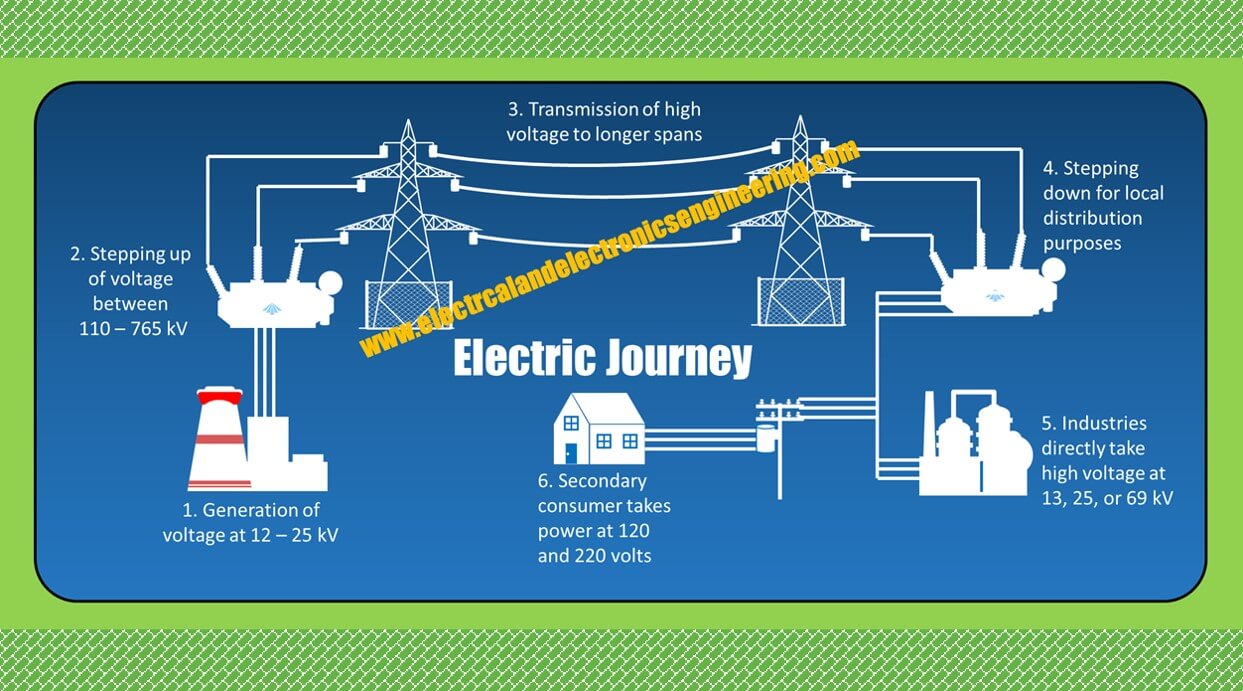
Electricity is generated in power stations where different energy sources are processed to obtain electrical energy from them. In this article, you’ll learn the journey of electricity from the power station to our homes.
- Power generation: Electrical power plants contain a turbine that is synchronized with the generator. First of all water (in case of the hydroelectric plant) or steam turbine (in case of steam power stations) is rotated. When the turbine rotates, its synchronized generator also rotates and produces electricity at a certain voltage level (usually 10 to 25 kV)
- Stepping up: The generated electricity at low voltage level has heavy losses if transmitted. Instead, the voltage is stepped up for transmission at large distances
- Transmission: Power is then transmitted from the generation station to substations that are located near cities
- Stepping down: The substations receive this high voltage, steps it down to a certain voltage level and sends it to final distribution stations, from where the industries and utilities receive the electricity at transmission voltages
- Primary distribution: Primary consumers receive power at high voltage level usually at 13 or 25 kV
- Final distribution: Consumer and households take power at voltage secondary voltage level (120 & 220)
The figure below graphically depicts the journey of electricity: