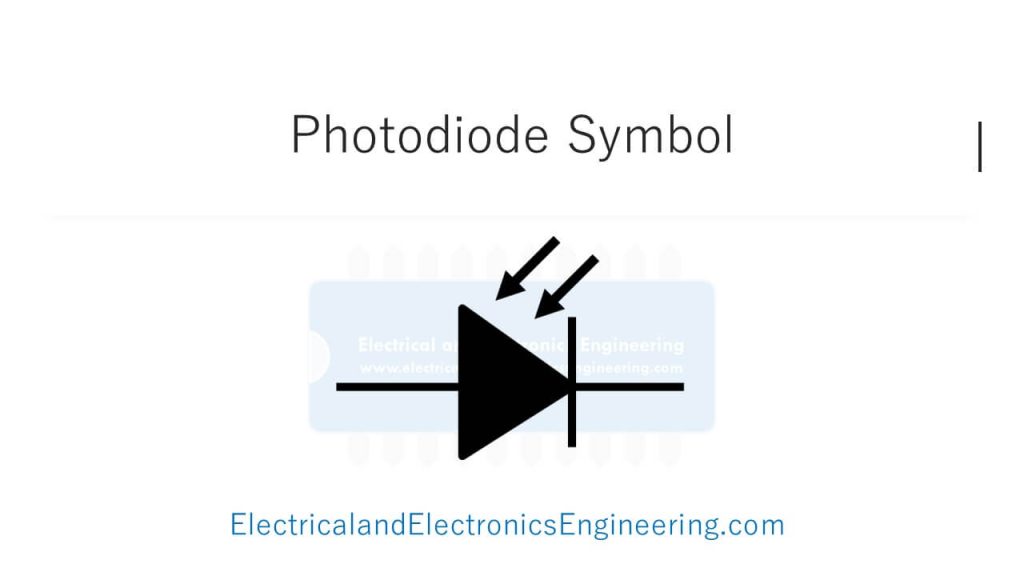
A photodiode is a semiconductor device that converts light energy into electrical current. It operates in reverse bias, meaning the cathode is connected to a higher voltage than the anode. When light photons strike the diode, electron-hole pairs are generated in the depletion region, resulting in a photocurrent flow. Photodiodes, such as optical communication systems, light sensors, and solar cells, are widely used in light detection and measurement applications. The symbol for a photodiode is similar to a regular diode but with an arrow pointing towards the cathode to indicate the current generation due to incident light.
Also, see the complete list of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Symbols here.
The figure below displays Photodiode Symbol.